Datasource
The datasource is used to set the database. Depending on how many connections your connector is designed for, up to 10 datasources can now be created. The following attributes can be configured in the datasource:
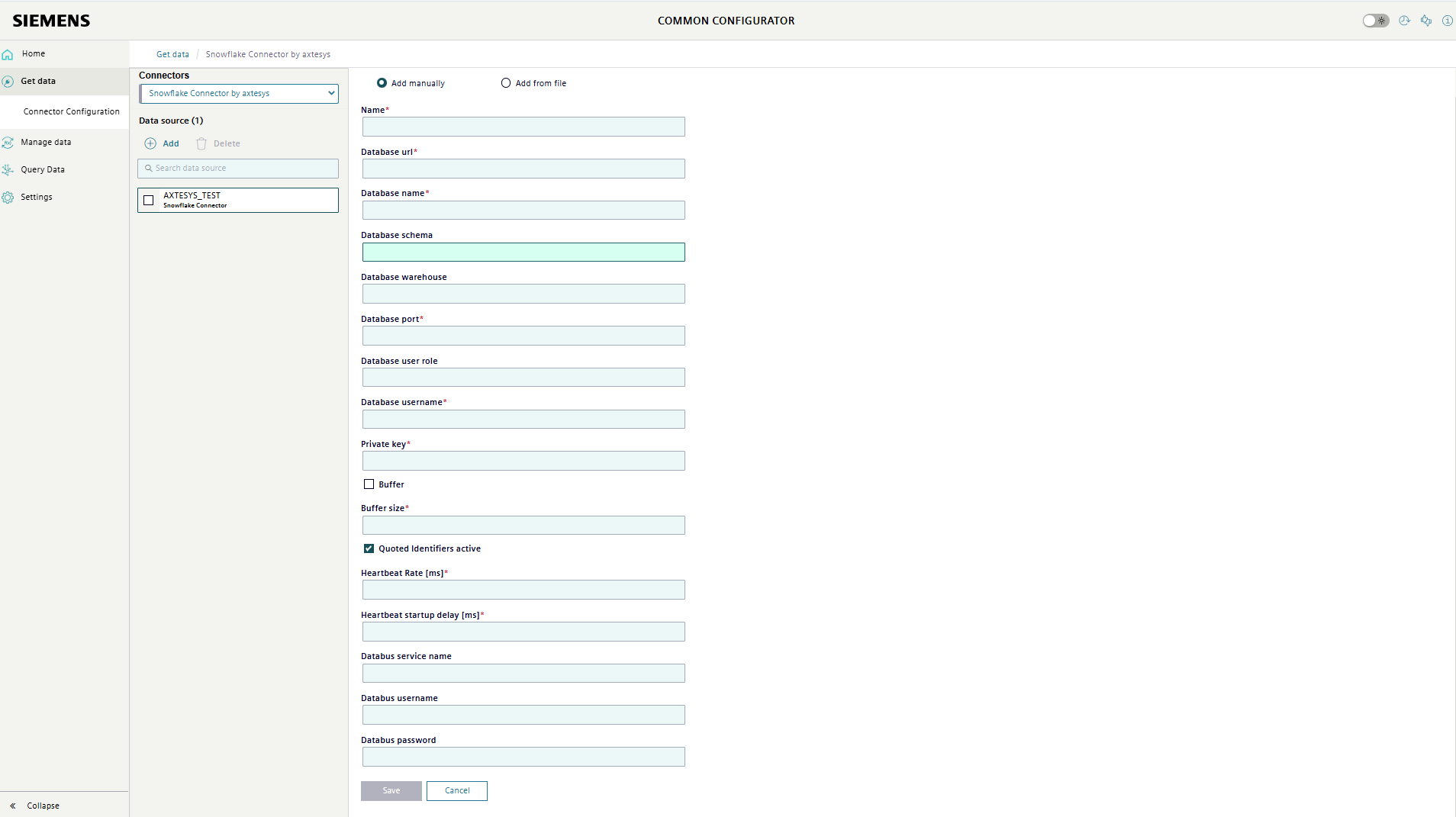
-
Name:
Each datasource has its own name, which can be freely chosen.
-
Database url:
The database URL is used to connect the Snowflake Connector to the database.
The url exists in the following format: {account_identifier}.snowflakecomputing.com. The "snowflakecomputing.com" is the set standard URL.
The account identifier has two specific fields that need to be set depending on what action to take. They can be found in the account details in SnowSight.
If the user wants to log in to an account or connect the connector, this form is used: https://<orgname>-<account_name>.snowflakecomputing.com.
The orgname is the name used by the users organization, which hold all accounts of the organization and is generated by the system when creating an account.
The account_name is the name given when creating the account and can be seen in the account details page.
The organization name combined with the account name form a unique identifier in Snowflake.
For more information, as well as examples of the URLs, please visit Snowflakes Account Guide.
Currently, the Snowflake Connector only supports Snowflake databases.
-
Database name:
The name of the database to which the Snowflake Connector should connect. The database must already be created and online so that the Snowflake connector can connect to it.
-
Database schema
The database schema which the Snowflake Connector should connect, the schema must already be created.
If not provided, then it's the default schema PUBLIC. Info about Snowflake
A Snowflake Database is a grouping of multiple schemas in a single account. Each of these schemas is a logical grouping of database object such as tables, and each of the schemas belong to a single database.
-
Database warehouse:
The database warehouse which the Snowflake Connector should connect, the warehouse must already be created.
if not provided, then it's the default schema COMPUTE_WH.
-
Database port:
The port of the database.
-
Database user role:
The role of the user which the Snowflake Connector should use for the user. if not provided then the default role of the user will be used.
-
Database username:
The user to connect to the database.
-
Private key
The connection to the snowflake database will be done using a secure key-pair authentication, without password and key rotation, you can find more information at Snowflake - configuring key pair authentication.
-
Buffer:
The buffer option is used to select between two insert modes. If this option is activated, a defined number of inserts will be collected before they are written to the database. If this option is not activated, buffering only takes place in the event of a connection to the database being lost.
-
Buffer size:
The buffer size is the number of inserts that are collected before they are transferred to the database. If the buffer option is not activated, the buffer size is ignored.
-
Quoted Identifier:
This encloses table and column names in quotation marks in all sql statements.
-
Heartbeat Rate
Specifies the interval in ms where the connector verifies the connection to the database.
-
Heartbeat startup delay
Specifies the delay after connector start until it starts performing connection checks to the database.
The optional fields "databus_service_name", "databus_username" and "databus_password" have been added to the datasource. These are used to ensure proper MQTT configuration to browse tags in the common configurator.
-
Databus service name
the databus host including the port
-
Databus username
The databus username which will be used to browse the tags.
-
Databus password
The databus password which will be used to browse the tags.